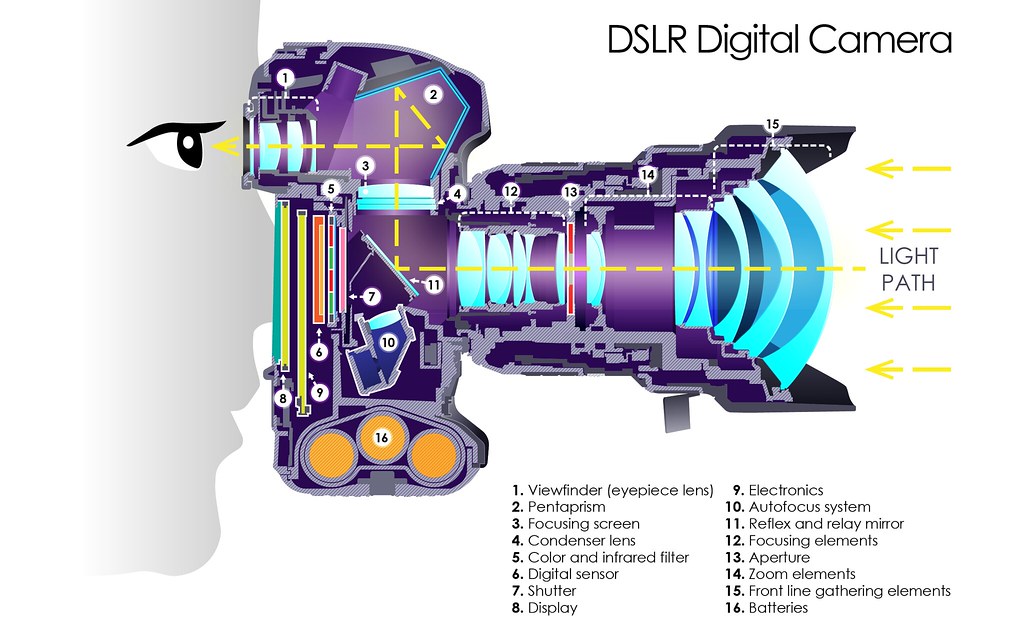
A DSLR, or digital single-lens reflex camera, works by using a combination of optics, electronics, and digital imaging technology to capture high-quality photographs.
When you look through the viewfinder of a DSLR, you are seeing an image that is being reflected by a mirror located inside the camera body. This mirror reflects the image coming through the lens up to a prism, which then redirects the light to your eye, giving you a clear and accurate view of the scene you are trying to capture.
When you press the shutter button to take a picture, the mirror flips up out of the way and allow the light to pass through the lens and onto the camera’s image sensor. The image sensor is made up of millions of tiny pixels, each of which records the amount of light that hits it.
After the image has been captured, it is processed by the camera’s onboard computer and stored on a memory card as a digital file. This digital file can then be transferred to a computer or other device for editing, sharing, or printing.

DSLRs offer a range of advanced features and settings that allow photographers to adjust various aspects of their images, including exposure, focus, depth of field, and white balance. They also typically have interchangeable lenses, which allow photographers to choose the best lens for a particular shot or subject.
Overall, DSLRs are popular among photographers for their versatility, image quality, and control over the creative process.